
For example, ERA-Interim (ERAI) provides certain variables as accumulations over time intervals and these must be disaggregated if instantaneous values are desired. (i) Technical delivery: available data are well documented but their structure largely reflects the needs and conventions common in atmospheric simulation, and as a consequence, individuals used to working with data from meteorological stations may find their handling difficult.
#Gmd speed time no root series#
Because meteorological time series that drive models are a major source of uncertainty, having multiple reanalysis products available for ensemble simulations is an important step in estimating and reducing overall simulation uncertainty.įour main challenges impede the use of reanalysis data for simulating point locations. For instance, they can be generated by varying the forcing data (e.g., Guo et al., 2018), the models themselves (e.g., Westermann et al., 2015 b) or the structure and parameters of a model (e.g., Gubler, 2013). Ensembles consist of multiple simulations for a given location and time that differ in one or more ways. The use of model ensembles is established to evaluate uncertainty or improve predictive accuracy in simulation studies (e.g., Tebaldi and Knutti, 2007). Their relative suitability for specific simulation studies and locations is likely to vary because they rely on different assumptions, parameterizations or assimilated input data, and these differences result in biases that are spatially heterogeneous and specific to one or several meteorological variables ( Decker et al., 2012 Zhang et al., 2016). Several global reanalysis products are available to drive simulations or ensembles of simulations. The suitability of reanalysis data for individual projects depends on the environment studied, the skill of the reanalysis in representing it and characteristics of the intended application.
#Gmd speed time no root software#
The software GlobSim, which is presented here, aims to contribute to overcoming this obstacle. Their application to point locations (e.g., Ekici et al., 2015 Westermann et al., 2016), however, is currently limited, likely because accessing data is technically involved. They assimilate a broad range of observations into numerical weather-prediction models, usually have coarse grid spacing (10–100 km) and are often used for large-area studies in atmospheric and hydrological modeling (e.g., Žagar et al., 2018 Albergel et al., 2018). In this context, global atmospheric reanalyses can substitute for lacking observations or supplement incomplete records. Because they require meteorological forcing – with daily or finer temporal resolution, for extended periods and without gaps – site-specific applications such as process studies or model testing are limited to few locations where high quality ground observations are available. Models that represent the interactions between the land surface and the atmosphere are often used to investigate biogeochemical, cryospheric and hydrologic phenomena.
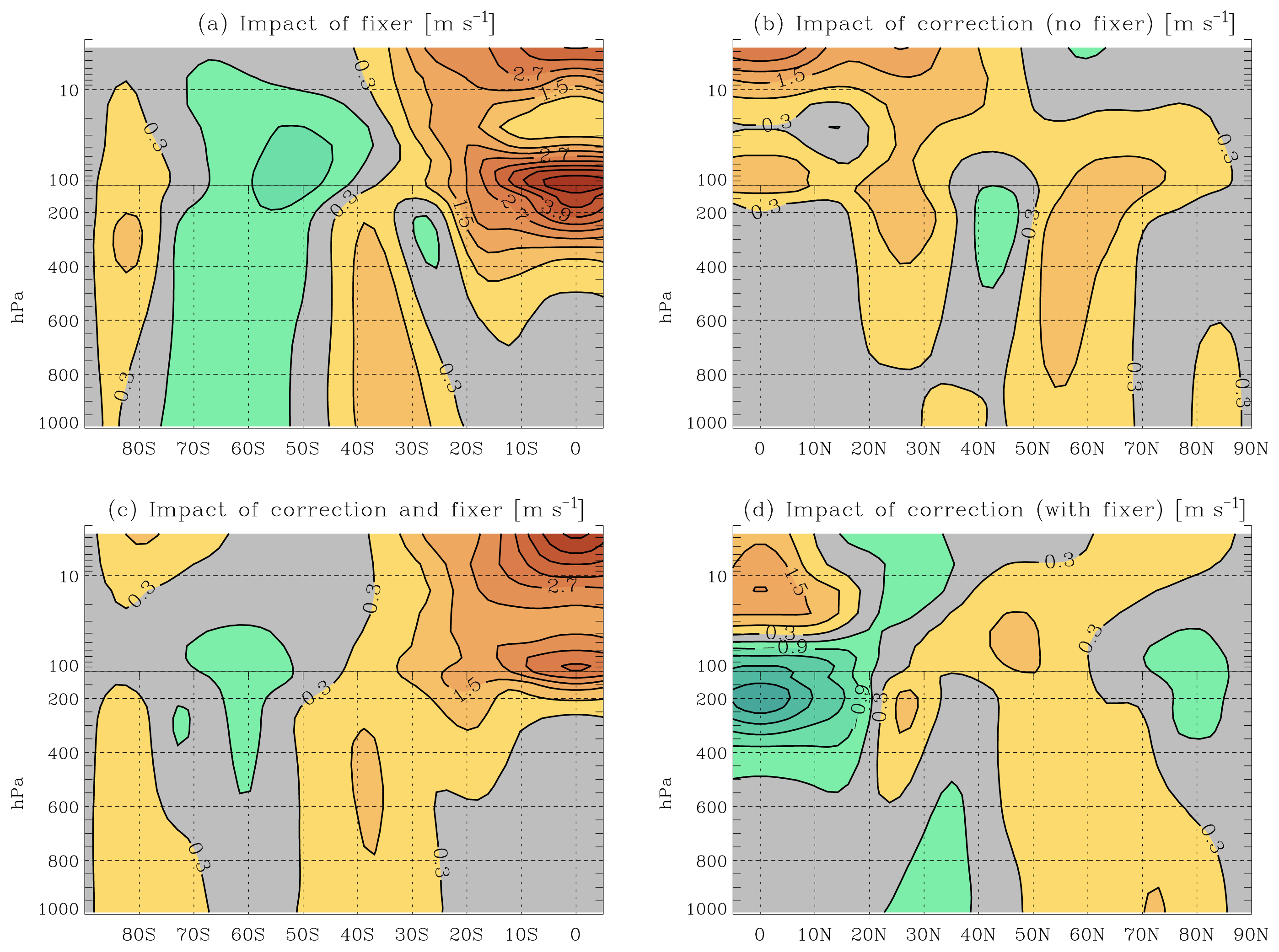
Ensemble means often yielded better accuracy than individual simulations and ensemble ranges additionally provide indications of uncertainty arising from uncertain input.īy improving the usability of reanalyses for research requiring time series of climate variables for point locations, GlobSim can enable a wide range of simulation studies and model evaluations that previously were impeded by technical hurdles in obtaining suitable data. Simulation results reproduced seasonal cycles and variation between terrain types well, demonstrating that GlobSim can support efficient land-surface simulations. We perform ensemble simulations of ground-surface temperature for 10 terrain types in a remote tundra area in northern Canada and compare the results with observations. The utility of GlobSim is demonstrated using an application in permafrost research.
The resulting data have consistent structure and units to efficiently support ensemble simulation. We present the software toolkit GlobSim, which automates the downloading, interpolation and scaling of different reanalyses – currently ERA5, ERA-Interim, JRA-55 and MERRA-2 – to produce meteorological time series for user-defined point locations. This is because technical challenges limit the ease with which reanalysis data can be applied to models at the site scale. Atmospheric reanalyses provide global coverage of relevant meteorological variables, but their use is largely restricted to grid-based studies. Corresponding observations, however, are unavailable in most locations, even more so, when considering the duration, continuity and data quality required. Simulations of land-surface processes and phenomena often require driving time series of meteorological variables.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
